
You may not notice any symptoms if only a small portion of your retina has detached. Retinal detachment can be caused by many things, it happens when your retina (a light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of your eye) is pushed out of its normal position. If you are experiencing symptoms it’s important to schedule an eye exam. When this happens, it can cause pain and vision problems. Some people are unable to produce normal tears or their tears evaporate too quickly. The eye constantly produces tears to reduce friction and keep vision sharp. It can be scary when we start noticing symptoms that pose a risk to our sight.ĭry eyes are a common condition that can cause discomfort and even vision loss. Call the nearest office to make an appointment.Our eyes and vision are one of the most important senses we have to take in the world around us.
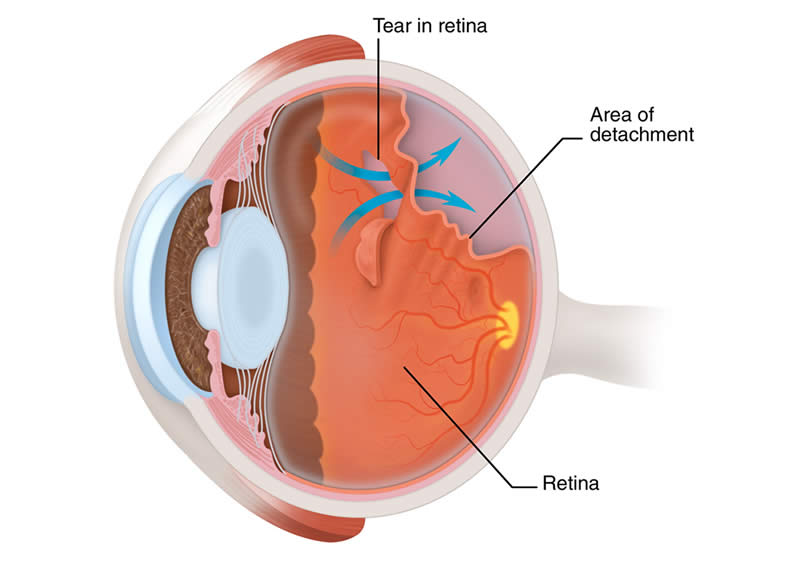
Make sure you understand your risk factors and the signs of a retinal detachment so you can take action quickly and save your sight.Īlso, make sure to schedule regular comprehensive eye exams so we can monitor and track your retinal health. If you have a family or personal history of retinal problems or extreme myopia, or you had a previous eye injury or surgery, your risk of a detached retina increases. Uncontrolled diabetes leads to abnormal blood vessel growth on your retina, which contributes to tractional and exudative retinal detachments. If you’re diabetic, keeping your blood sugar well-controlled is important to eye health. Most rhegmatogenous retinal detachments are simply the result of age-related changes to your vitreous fluid - the gel substance that fills your eyeballs. Your chances of developing a retinal detachment increase with age. It’s more often due to another injury or eye conditions like macular degeneration. ExudativeĮxudative retinal detachment occurs when you have fluid between your retina and the wall of blood vessels, but no tear in the retina that allows fluid to accumulate. Scar tissue could develop because of leaking blood vessels caused by diabetic retinopathy or extreme myopia (nearsightedness). TractionalĪ tractional retinal detachment is caused by scar tissue on your retina. This creates pressure that pulls the retina away from the underlying blood vessels and tissues. It occurs when a small hole in your retina allows fluid to accumulate underneath it. RhegmatogenousĪ rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is the most common type. There are three types of retinal detachment : rhegmatogenous, tractional, and exudative. In some cases, your surgeon places a scleral buckle around your eye to keep your retina from moving while your eye heals. They remove the vitreous that’s pulling on your retina and replace it with a gas or oil bubble that guides your retina back into place. In most cases, our ophthalmologists perform emergency surgery to repair your eye. With offices in Dallas, Desoto, Plano, Mesquite, Waxahachie, Texas, our team of expert ophthalmologists can offer convenient, same-day diagnosis and treatment for eye emergencies like a detached retina. If you develop any of these symptoms, call our team here at Retina Specialists and get immediate treatment and advice. What to do if you think you have a retinal detachment These symptoms can be disorienting, but don’t panic - take action. A shadow curtain over your visual field.

It might look like a waterfall of floaters sliding over your field of vision. For example, the most common warning sign is a sudden increase in the number of floaters in your eye. Retinal detachment is when the wall of retinal cells pulls away from the layer of blood vessels that nourish it.Ī detached retina doesn’t cause any eye pain or even a headache, but it can change your vision. Your retina is the part of the back of your eye where light focuses and is converted to electrical signals that travel along your optic nerve to your brain. We now share the symptoms of a detached retina so you know what to do in the case of this eye emergency. Everyone see little specks or strings floating through their vision from time to time, but a sudden increase of your floaters could be a sign of retinal detachment - an eye emergency that could result in blindness.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
